In today's fast-paced technological landscape, the importance of efficient & effective Test Data Management (TDM) simply cannot be highlighted enough. As the digital footprint of companies increases, so does the complexity of its test data & the management thereof. When looking at international test data surveys such as the most recent World Quality Report and other Verified Market Reports from 2023, it is clear that many companies around the globe have increasingly started to realise the importance of a mature TDM solution. The ’23-24 World Quality Report indicates that 69% of its respondents were in the process of adopting an enterprise-wide data provisioning strategy, compared to only 31% in the previous report.
While the uptake of TDM may be increasing, many companies will still be left frustrated without a proper TDM strategy and by the challenges of poorly managed test data. TDM is a strategic process and to reap its full benefits companies should understand exactly what TDM is, its typical challenges, how they might benefit from TDM, and what a typical TDM strategy might look like.
What is Test Data Management?
Test data management (TDM) can be summarised as the process of creating, maintaining, and controlling data sets required for software testing purposes. It involves ensuring that the right test data is available in the right format at the right time to help facilitate accurate and comprehensive testing of software applications. TDM can encompass various tasks, including obfuscation of Personal Identifiable Information (PII), synthetic test data generation, data subsetting, refreshing of datasets and the automated provisioning of test data to non-production environments. Effective TDM is crucial for achieving reliable test results, identifying defects, and ensuring the overall quality of software products.
Challenges of TDM:
The adoption of TDM may be hampered by common challenges such as a limited budget and resources, resistance to change, a lack of TDM expertise, and difficulty in integration with legacy systems, not to mention the complexities of data synchronisation across multiple systems and environments.
Organisations might have adopted TDM but their approach might be inefficient, which bring its unique challenges, often resulting in delayed time-to-market & increased costs. Below are 8 typical challenges that companies often face due to inefficient TDM:
- Delays in Test Data Provisioning: The insufficient and often manual provisioning of test data can cause delays in the testing process, causing project timelines to slip.
- Data Inconsistencies Across Test Environments: Test data can vary between test environments, making it difficult to re-use the same test cases across all test environments.
- Security & Compliance Risks: Inability to manage and protect personally identifiable information (PII) can lead to non-compliance with data privacy regulations such as POPIA and GDPR.
- Limited Testing Coverage: The lack of diverse test data could restrict the scope of testing scenarios, therefore exposing the risk of leaving potentially critical defects undetected.
- Inefficient Resource Utilisation: Manual test data creation can often be time-consuming, error-prone & demoralising to testers and developers. By not leveraging from the automation of TDM tasks, testers and developers often spend excessive time on data preparation tasks rather than actual testing and development work.
- Difficulty in Scaling Test Environments: Scaling test environments becomes challenging, hindering the ability to handle large-scale testing efforts.
- Difficulty in Data Refresh: Frequent updates to test data & database schema changes (in order to reflect changes in the Production environment) may be manual, cumbersome and prone to errors.
- Lack of Data Versioning: The lack of mature TDM will present challenges in managing different versions of test data, impeding regression testing and historical analysis.
Features and Benefits of Test Data Management
A mature TDM solution will enable the efficient, secure, and compliant management of test data, and ultimately improve software quality and development productivity. The features and benefits of TDM make it clear that it is an essential component in today’s technology landscape with its increasing complexity, such as the increasing focus on data privacy and compliance, shift-left practices, focus on DevOps and CI/CD pipelines, growing adoption of test automation, and the emergence of modern technologies like AI and ML.
- Data Obfuscation is the application of obfuscation techniques to protect PII to comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and POPIA.
- Data Subsetting reduces the size of the test database by only keeping the relevant test data required for testing purposes, which reduces storage costs and speeds up test data provisioning.
- Synthetic Data Versioning is the generation of realistic artificial test data which enables increased test coverage.
- Data Profiling maps the relationships between tables in a database and identifies PII for a better understanding of test data and where PII resides within the test data landscape.
- Virtualised Databases enable the quick creation of personal databases that can easily be recreated using a baseline database. This brings cost savings due to the low infrastructure footprint of virtual databases.
- Data Provisioning enables the automated delivery of test data across various testing environments which saves time and reduces human error.
- Self-service Access allows users to find and reserve specific sets of test data. This prevents jeopardised test results due to multiple testers using the same data set simultaneously.
- Data Refreshes keep test data synchronised with changes in Production, which enables testers to test using fresh data and the latest database schemas.
The Need for a TDM Strategy
A well-defined TDM strategy (and the proper execution thereof) is a critical component to addressing your test data challenges. By implementing a robust TDM strategy, organisations can streamline testing processes, minimise errors and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their software testing efforts.
At a high level, a mature TDM strategy could be separated into 2 core phases: Phase One lays the foundation through initiation and planning. During this phase, requirements and scope are determined, TDM tool selection is made, and a delivery roadmap is created:
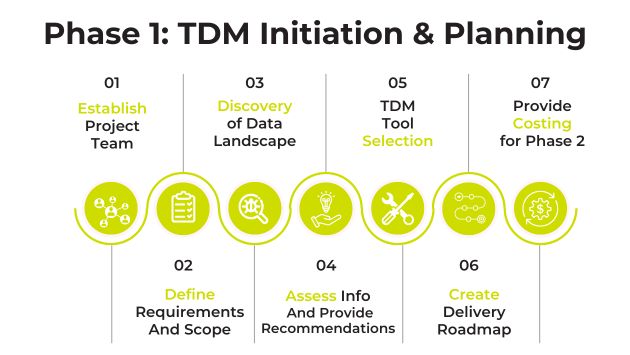
Phase Two sees the deployment and adoption of the TDM strategy: the TDM tool is installed and configured, certain features are implemented based on recommendations made in Phase One, it is tested and validated as it is gradually rolled out, and it is monitored and optimised. A post-implementation review should be performed to assess the success of the TDM rollout.

TDM for success in a competitive marketplace
In an era where data-driven decision-making and rapid software delivery are paramount, organisations must recognise the critical role that test data management plays in achieving these goals. By investing in a comprehensive TDM strategy, companies can streamline testing processes, improve software quality, and ultimately drive better business outcomes. As such, prioritising test data management within organisations is not merely an option but a necessity for success in today's dynamic and competitive marketplace.







